Information provided is based on research. We strive for accuracy, but consult professionals for personalized advice. External links are not under our control. See our Privacy Policy for details.
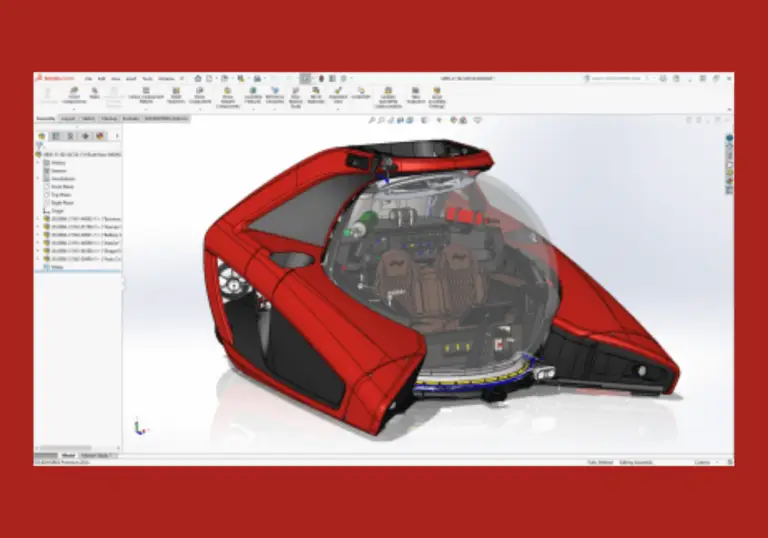
SolidWorks is a powerful 3D computer-aided design (CAD) software primarily used by engineers, designers, and architects for designing and modeling mechanical parts, assemblies, and drawings. Developed by Dassault Systèmes, SolidWorks has become one of the most popular CAD tools for product design and development, particularly in industries like automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and consumer products.
Launched in 1995, SolidWorks has revolutionized how professionals handle mechanical design by offering a highly interactive, parametric modeling environment. Unlike traditional 2D drafting tools, it allows users to create detailed 3D models, simulate real-world behaviors, and generate drawings with extreme precision. This article explores the key features, applications, and benefits of SolidWorks, shedding light on its impact in modern engineering and design.
Key Features of SolidWorks
1. Parametric Design
SolidWorks is a parametric modeling tool, meaning the design is built using a series of interconnected features and dimensions. This parametric nature allows users to modify designs easily—any changes made to one part of the model automatically update the entire design, saving time and effort.
2. 3D Modeling and Design
The core function of SolidWorks is 3D modeling. It provides an intuitive interface that allows users to create precise 3D models of individual components and entire assemblies. These models can be viewed from different angles, rotated, zoomed, and modified to meet design requirements.
3. Simulation and Testing
SolidWorks includes simulation tools for testing models under real-world conditions. Users can perform structural, thermal, fluid, and motion analyses, which help to verify that designs are strong, functional, and efficient. This feature minimizes the need for physical prototypes, which reduces costs and speeds up the design process.
4. Drafting and Detailing
SolidWorks offers advanced tools for creating 2D drawings based on 3D models. These drawings include dimensions, annotations, and tolerances, making it easier to communicate design intent to manufacturers. The software ensures that all drawings are fully associative, meaning any changes to the 3D model automatically update the 2D drawing.
5. Collaboration and File Sharing
SolidWorks supports multiple file formats, enabling collaboration between designers and engineers using different CAD tools. It also integrates with Product Data Management (PDM) systems, which allows team members to track changes, manage versions, and share files securely across departments or with external clients.
6. Additive Manufacturing Integration
SolidWorks supports additive manufacturing (3D printing) workflows by enabling users to optimize models for printing and output them in formats compatible with 3D printers. This capability is becoming increasingly important in prototyping and custom manufacturing.
7. Libraries and Standard Components
SolidWorks provides a vast library of pre-designed components such as fasteners, gears, bearings, and more, which users can quickly incorporate into their models. These libraries save time and ensure that the parts used in designs meet industry standards.
8. Cloud Collaboration (3DEXPERIENCE)
Dassault Systèmes offers cloud-based collaboration through its 3DEXPERIENCE platform, which integrates seamlessly with SolidWorks. This feature allows teams to work together on projects from anywhere, enhancing communication, reducing version conflicts, and speeding up development times.
Applications of SolidWorks
SolidWorks is used in various industries for a wide range of applications, including but not limited to:
1. Automotive Design
In the automotive industry, SolidWorks plays a crucial role in designing everything from car parts to entire vehicle assemblies. Engineers use it to create and test components such as engines, transmissions, and suspensions, ensuring that they meet safety and performance standards.
2. Aerospace and Defense
Aerospace engineers use SolidWorks to design aircraft components, satellites, and defense equipment. The software’s ability to simulate stress, thermal conditions, and aerodynamics helps in creating designs that can withstand harsh conditions.
3. Consumer Product Design
Many companies rely on SolidWorks for the design and development of consumer goods, from household appliances to electronics. The software allows designers to create aesthetically pleasing, functional, and cost-effective products.
4. Industrial Machinery
SolidWorks is also widely used in the development of industrial machinery. It provides tools for designing large mechanical systems, verifying performance through simulation, and generating detailed manufacturing drawings.
5. Medical Devices
In the healthcare industry, SolidWorks is used for designing medical devices and equipment. Its simulation capabilities help engineers ensure that these products are safe, durable, and easy to manufacture.
6. Education and Research
SolidWorks is a valuable tool in educational institutions and research labs, where students and researchers use it to learn mechanical design principles and conduct experiments in various fields of engineering and science.
Benefits of Using SolidWorks
1. Time and Cost Efficiency
By providing an integrated platform for design, simulation, and documentation, SolidWorks helps users save significant time and costs. Its parametric nature allows for quick modifications, and its simulation tools reduce the need for expensive physical prototypes.
2. Precision and Accuracy
SolidWorks provides unparalleled precision in design, ensuring that every component and assembly is accurate to the smallest detail. This accuracy is essential in industries where even the smallest design flaw can lead to costly errors or safety risks.
3. Innovation
SolidWorks allows designers to push the boundaries of innovation. With advanced features such as topology optimization and generative design, users can explore new design possibilities and optimize components for weight, strength, and efficiency.
4. Enhanced Collaboration
SolidWorks supports collaboration across departments and locations, enabling teams to work together on complex projects seamlessly. The software’s integration with cloud-based platforms like 3DEXPERIENCE makes it easier to share files, track changes, and manage projects.
5. Comprehensive Support and Training
SolidWorks comes with extensive support resources, including tutorials, user forums, and certification programs. Dassault Systèmes also offers regular updates and new features, ensuring that users always have access to the latest tools and technologies.
Facts and Statistics
- Market Share: SolidWorks holds a significant portion of the CAD market, with an estimated 3.2 million users worldwide as of 2021, spread across 80 countries .
- Job Demand: According to data from Glassdoor, the demand for SolidWorks skills continues to rise, with over 20,000 job postings mentioning proficiency in SolidWorks .
- Cost Savings: A study by Lifecycle Insights found that companies using SolidWorks reported an average of 30% reduction in development costs and a 20% decrease in time-to-market .
- Industry Adoption: SolidWorks is widely used across automotive, aerospace, defense, consumer goods, and healthcare industries, accounting for 60% of its user base .
Conclusion
SolidWorks is a versatile and powerful tool that has become indispensable in the world of mechanical design and engineering. Its ability to create precise 3D models, simulate real-world conditions, and streamline the entire design process makes it a top choice for professionals across various industries. Whether you are designing automotive parts, consumer products, or complex industrial machinery, SolidWorks offers the tools and features you need to bring your ideas to life with speed, accuracy, and efficiency.
With a growing user base and increasing demand for SolidWorks skills, it’s clear that this software will continue to play a vital role in shaping the future of design and engineering.